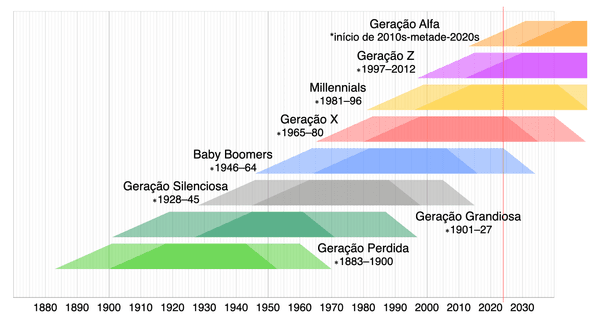
The term "Western world" encompasses regions of Western Europe, North America, and Australasia. Within these areas, significant geographical and cultural variations exist, making any generational list broadly indicative and somewhat generalized. The current descriptions of these generational cohorts, often utilized in media and advertising, are partially derived from the Strauss–Howe generational theory and align with the principles of the pulse-rate hypothesis.
1. The Lost Generation
The Lost Generation, also referred to as the "Generation of 1914" in Europe, is a term coined by Gertrude Stein to describe individuals who served in World War I. This cohort is characterized as those born between 1883 and 1900, who reached adulthood during the tumultuous times of World War I and the Roaring Twenties.
2. The Greatest Generation
Known in American contexts as the G.I. Generation, the Greatest Generation comprises veterans who fought in World War II. This group includes individuals born from 1901 to 1927. The older segment of this generation, often called the Interbellum Generation, came of age during the Roaring Twenties, whereas the younger members faced the challenges of the Great Depression and World War II. The term gained popularity through journalist Tom Brokaw's book, The Greatest Generation.
3. The Silent Generation
The Silent Generation, sometimes referred to as the Lucky Few, includes those who came of age in the post-World War II period. Individuals in this cohort were born between 1928 and 1945. In the United States, this generation encompasses many who served in the Korean War and a significant number who participated in the Vietnam War.
4. Baby Boomers
Baby boomers, often abbreviated to Boomers, are individuals born in the aftermath of World War II, specifically from 1946 to 1964. This period saw a notable increase in birth rates, resulting in a substantial demographic cohort. In the U.S., many older boomers were involved in the Vietnam War or engaged in the counterculture movements of the 1960s, while younger boomers, sometimes referred to as Generation Jones, grew up during the economic stagnation of the 1970s.
5. Generation X
Generation X, commonly abbreviated as Gen X, follows the Baby Boomers and is generally defined as those born between 1965 and 1980. The term has been applied to various subcultures and countercultures since the 1950s. In the U.S., members of this generation are sometimes called the "baby bust" generation due to the decline in birth rates that followed the baby boom.
6. Millennials
Also known as Generation Y or Gen Y, Millennials are the cohort that follows Generation X, typically defined as those born from 1981 to 1996. According to the Pew Research Center, this generation includes individuals born in this timeframe and, as of 2019, outnumbered Baby Boomers in the United States, with approximately 72.1 million Millennials compared to 71.6 million Boomers.
7. Generation Z
Generation Z, often abbreviated as Gen Z and colloquially referred to as Zoomers, includes individuals born from 1997 to the early 2010s. The Pew Research Center defines this generation as spanning from 1997 to 2012. This definition has been acknowledged by both the United States Library of Congress and Statistics Canada. A 2022 report from the U.S. Census Bureau identifies Generation Z as those born from 1997 to 2013. Members of this generation experienced the onset and consequences of the COVID-19 pandemic during their childhood or early adulthood.
8. Generation Alpha
Generation Alpha, or Gen Alpha, is the cohort that follows Generation Z. Researchers and popular media generally consider the early 2010s as the starting point for this generation, with the mid-2020s marking its conclusion. Generation Alpha is notable for being the first generation born entirely in the 21st century. By 2015, approximately 2.5 million individuals were born each week globally, and it is projected that Gen Alpha will reach nearly two billion in size by 2025.